Exploring the disparities between startup businesses and small businesses sheds light on the distinct paths they tread towards success. This comparison delves into the nuances of their operations, goals, and strategies, offering a comprehensive view of the entrepreneurial landscape.
Definition of Startup Business and Small Business
A startup business is a newly established company designed to rapidly grow and scale, often with innovative products or services. These businesses typically operate in an environment of uncertainty and aim to disrupt existing markets.
A small business, on the other hand, is a privately owned enterprise with a limited number of employees and relatively low sales volume. These businesses are typically more established and focus on serving a local or niche market.
Characteristics and Goals
- Startup Business:
- High growth potential
- Focus on innovation and disruption
- Risk-taking and experimentation
- Seeking funding from venture capitalists
- Goal of scaling rapidly and expanding globally
- Small Business:
- Stable and steady growth
- Local or niche market focus
- Limited resources and budget
- Owner-operated or family-run
- Goal of sustainability and profitability
Funding and Capital
When it comes to funding and capital, startup businesses and small businesses often have different approaches and challenges.
Funding Sources for Startups
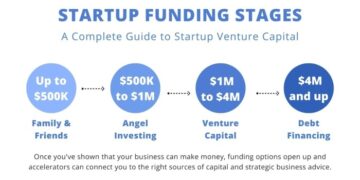
Startups typically rely on a variety of funding sources to get off the ground and grow:
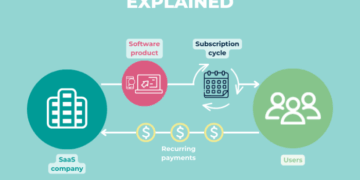
- Venture capital: Investors provide funding in exchange for equity in the company.
- Angel investors: High-net-worth individuals who invest their personal funds in startups.
- Crowdfunding: Platforms where individuals can contribute funds to support a startup.
- Accelerators and incubators: Programs that offer funding, mentorship, and resources to startups in exchange for equity.
Acquiring Capital for Small Businesses
Small businesses, on the other hand, typically acquire capital through more traditional means:
- Bank loans: Small businesses can apply for loans from financial institutions to fund their operations.
- Personal savings: Many small business owners use their own savings to start and grow their businesses.
- Grants and subsidies: Small businesses may qualify for government grants or subsidies to support their growth.
- Revenue reinvestment: Small businesses often reinvest profits back into the business to fuel growth.
Financial Challenges for Startups vs Small Businesses
Startups and small businesses face different financial challenges:
- Startups often struggle to secure funding in the early stages and may face cash flow issues as they grow.
- Small businesses may find it challenging to access affordable financing and manage cash flow effectively.
- Startups need to demonstrate high growth potential to attract investors, while small businesses focus on profitability and sustainability.
- Small businesses may have limited resources to weather economic downturns, while startups may have more flexibility to pivot and adapt.
Growth and Scalability
When it comes to growth and scalability, startups and small businesses often have different approaches and priorities. Startups typically aim for rapid growth and scalability to quickly capture market share and attract investors. On the other hand, small businesses focus on steady growth and sustainability to ensure long-term success and stability in the market.
Strategies for Startups
Startups often utilize innovative strategies to achieve rapid growth and scalability. Some common approaches include:
- Aggressive marketing campaigns to quickly build brand awareness and acquire customers
- Rapid product development and iteration to stay ahead of competitors and meet evolving market demands
- Seeking venture capital funding to fuel expansion and accelerate growth
- Strategic partnerships and collaborations to access new markets and distribution channels
Strategies for Small Businesses
Small businesses focus on sustainable growth and often employ the following strategies:
- Building strong customer relationships and loyalty to drive repeat business and word-of-mouth referrals
- Gradual expansion into new markets or product lines to ensure consistent revenue growth
- Bootstrapping or using traditional bank loans to fund growth initiatives and avoid excessive debt
- Emphasizing quality over quantity to maintain a loyal customer base and positive reputation
Innovation and Risk-Taking
Innovation and risk-taking are key components that differentiate startups from small businesses. Startups are known for their emphasis on innovation and their willingness to take risks in pursuit of growth and success.Small businesses, on the other hand, tend to focus on maintaining stability and consistency, often avoiding high-risk ventures that could jeopardize their established operations.
Emphasis on Innovation in Startups
Startups are built on the foundation of innovation, constantly seeking new and creative solutions to address existing problems or meet market demands. They are known for disrupting traditional industries with groundbreaking ideas and technologies. For example, startups like Uber and Airbnb revolutionized the transportation and hospitality industries, respectively, by introducing innovative business models and technologies.
Risk-Taking Nature of Startups
Startups are inherently risky ventures, as they often operate in uncharted territories with uncertain outcomes. Entrepreneurs behind startups are willing to take calculated risks, such as investing in unproven ideas or entering competitive markets, in the hopes of achieving rapid growth and success.
This risk-taking attitude sets startups apart from small businesses that prioritize stability and gradual growth.
Innovative Practices in Startups vs Small Businesses
- Startups often invest heavily in research and development to create unique products or services that differentiate them from competitors, while small businesses may focus on refining existing offerings.
- Startups are more likely to embrace emerging technologies and trends to stay ahead of the curve, while small businesses may be more hesitant to adopt new technologies due to cost or uncertainty.
- Startups are open to experimenting with new business models and strategies, such as subscription-based services or peer-to-peer platforms, whereas small businesses may stick to traditional methods that have proven successful in the past.
Closing Notes
In conclusion, the contrast between startup businesses and small businesses underscores the diverse approaches taken in the business world. Understanding these key differences can aid aspiring entrepreneurs in navigating their own ventures with clarity and purpose.
FAQ Insights
What defines a startup business?
A startup business is typically a newly established company with innovative ideas aiming for rapid growth and disruption in the market.
How is a small business different from a startup?
A small business is usually a more established, traditional business focusing on steady growth and sustainability rather than rapid expansion.
What are the common funding sources for startups?
Startups often rely on venture capital, angel investors, crowdfunding, or accelerator programs for funding.
How do small businesses usually acquire capital?
Small businesses typically obtain capital through bank loans, personal savings, or small business grants.
What are some examples of innovative practices in startups compared to small businesses?
Startups may engage in disruptive technologies, agile methodologies, and rapid experimentation, while small businesses may focus on traditional marketing strategies and incremental improvements.