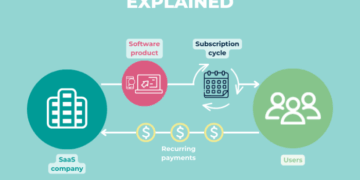
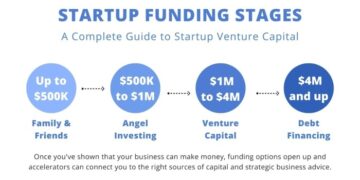
Exploring the legal landscape for startup businesses in the US and Europe, this introduction sets the stage with valuable insights and key information to captivate readers.
Providing a detailed overview of the legal requirements and considerations for startups in both regions, this guide aims to shed light on the essential aspects of setting up and operating a business.
Legal requirements for a startup business in the US
Starting a business in the US involves several legal requirements that entrepreneurs need to adhere to in order to operate legally and avoid any potential issues down the road.
Registering a Business Entity in the US
When starting a business in the US, one of the first steps is to register your business entity with the appropriate state authorities. This typically involves choosing a business structure and registering with the Secretary of State or similar agency.
The process may vary depending on the state where you are establishing your business.
Types of Business Structures Available for Startups in the US
There are several types of business structures available for startups in the US, including sole proprietorships, partnerships, limited liability companies (LLCs), and corporations. Each structure has its own advantages and disadvantages in terms of liability protection, tax implications, and operational flexibility.
Tax Implications of Different Business Structures in the US
The tax implications of different business structures in the US vary depending on the type of entity you choose. For example, sole proprietorships and partnerships are pass-through entities, where profits and losses are passed through to the owners' individual tax returns.
On the other hand, corporations are taxed separately from their owners, leading to potential double taxation.
Licenses and Permits Required for Operating a Startup in the US
In addition to registering your business entity, startups in the US may need to obtain various licenses and permits to operate legally. These requirements can vary based on the industry, location, and nature of the business. Common examples include business licenses, sales tax permits, health department permits, and professional licenses.
Legal requirements for a startup business in Europe
In Europe, starting a business involves navigating through various legal requirements that differ from those in the US. Understanding these requirements is crucial for the successful establishment and operation of a startup in Europe.
Steps to establish a business entity in a European country
When establishing a business entity in a European country, startups need to consider the following key steps:
- Choose the legal structure: Decide on the most suitable legal structure for your business, such as a sole proprietorship, partnership, limited liability company (LLC), or corporation.
- Register the business: Register the business with the relevant authorities in the country where you plan to operate. This may involve obtaining a business license, tax identification number, and other permits.
- Comply with local regulations: Ensure compliance with local regulations regarding taxation, employment, and other legal requirements specific to the country.
- Open a business bank account: Set up a business bank account to manage finances and facilitate transactions related to the business.
Intellectual property laws differences between the US and Europe
There are significant differences in intellectual property laws between the US and Europe, including:
- In Europe, trademarks are registered at the European Union Intellectual Property Office (EUIPO) for protection across EU member states, while in the US, trademarks are registered with the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO).
- Europe follows the "first-to-file" system for patents, meaning that the first person to file a patent application is granted the patent, whereas the US follows a "first-to-invent" system.
- Copyright laws in Europe and the US have differences in terms of duration, scope of protection, and copyright exceptions.
GDPR compliance for startups operating in Europe
Startups operating in Europe must comply with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) to protect the personal data of individuals. Key aspects of GDPR compliance include:
- Obtaining explicit consent from individuals before collecting their personal data.
- Implementing measures to ensure the security and confidentiality of personal data.
- Appointing a Data Protection Officer (DPO) if the startup processes large amounts of personal data.
Labor laws and regulations applicable to startups in Europe
Startups in Europe must adhere to labor laws and regulations to ensure fair treatment of employees and compliance with employment standards. Some key aspects of labor laws applicable to startups in Europe include:
- Minimum wage requirements vary across European countries and must be followed by startups when hiring employees.
- Working hour regulations, including maximum weekly working hours and minimum rest periods, are set by each country's labor laws.
- Employee rights, such as paid leave, maternity/paternity leave, and anti-discrimination laws, must be upheld by startups in Europe.
Final Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the legal requirements for startup businesses in the US and Europe is crucial for success and compliance. By navigating the intricacies of business registration, structure, tax implications, and regulatory compliance, entrepreneurs can pave the way for a prosperous venture.
FAQ Explained
What are the key steps to register a business entity in the US?
Registering a business entity in the US involves choosing a business structure, obtaining an EIN, and registering with the appropriate state authorities.
What licenses and permits are typically required for startups in Europe?
The licenses and permits needed for startups in Europe vary by country and industry, but common ones include a business license, health department permits, and zoning permits.
How does GDPR compliance impact startups operating in Europe?
GDPR compliance is crucial for startups in Europe, as it involves protecting personal data, obtaining consent for data processing, and ensuring data security measures are in place.